Distributed Systems
Distributed Systems distribute jobs or computation among several physical processors. So, several processors interconnected with each other by a communication network forms a Distributed System.
The processors in a Distributed System may vary in Size and Function. They may include small Microprocessors, Workstations, Mini Computers and even Large general purpose computer systems. These processors can be referred by a number of different names, i.e. Sites, Nodes, Computers, Machines etc. Generally, one site, the Server, has a resource that another site, the client (user) would like to use. It is the purpose of the Distributed System to provide an efficient and convenient environment for this type of Sharing of Resources.
Two schemes are mostly used for building Distributed Systems.
i) Tightly Coupled System
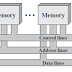
In a Tightly Coupled System, the processors share Memory and a Clock. In such kind of Multiprocessor Systems, communication takes place through the Shared Memory.
ii) Loosely Coupled System
In a Loosely Coupled System, the processors do not share Memory or Clock, and each processor has its own Local Memory, and the processors communicate with each other through various communication lines i.e. High-Speed Buses or Telephone Lines.
Reasons for building Distributed Systems
A Distributed System is designed due to the following reasons
1) Resource Sharing
In a Distributed System, users can share or use the resources available at other sites or machines. A user working in a Distributed Environment can use the Printer (resource) connected to some other computer. Similarly, a user can Access files present on some other computer in a Distributed Environment. So, Processing information in a Distributed Database, Printing files at remote sites and using remote specialized hardware are all examples of resource sharing in a Distributed System.
2) Computation Speed Up
Computation speed can be increased in a Distributed Environment if a computation can be partitioned into a number of sub-computations that can run concurrently.
Load Sharing If a particular site is overloaded with jobs, then some of them can be moved or transferred to other sites in the Distributed System that are not overloaded or are lightly loaded. This movement of jobs is called Load Sharing.
3) Reliability
High Reliability is achieved in Distributed Systems that if one site fails due to any reason, then the remaining sites can continue operating.
If a system is composed of a number of small machines and each of which is responsible for some important system function than a single failure (hardware or software) in that environment may cause the halt of the whole system.
On the other hand, Distributed Systems are reliable in a way that the system can continue its operation even if some of the sites have failed due to any reason or have stopped working.
4) Communication
Distributed Systems provides a way or mechanism that programs can exchange data with one another. A user can transfer files to a system that is geographically located at a distant place. Similarly, electronic mail provides a way of communication with other users working at remote sites.