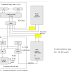
Process Control Block (PCB)
Every process in Operating System has its Processor Task Control Block. A Process Control Block or PCB is basically a record containing different kinds of information about a specified process.
Different kinds of information contained in a PCB are
q Process State Ready, Running or Waiting
q Program Counter Indicating the address of the next instruction that will be executed for the process.
q Accounting Information includes the amount of CPU and real time used. Similarly information about job or process number etc.
q Registers depend upon the architecture of the system. Registers include accumulators, Index registers, stack pointers and general purpose registers etc.
In a computer, A Register is one of a small set of data holding places that are part of a computer microprocessor. Registers provide a place for passing data from one instruction to the next sequential instruction or to another program that the operating system has just given control to. A register must be large enough to hold an instruction - for example, in a 32 -bit instruction computer, a register must be 32 bits in length. In some computer designs, there are smaller registers - for example, half-registers - for shorter instructions. Depending on the processor design and language rules, registers may be numbered or have arbitrary names.
q Scheduling Information contains information about the priority of the process etc.
q Memory Management Information contains information about limit registers or Page tables etc.
q I/O Status contains information about the requests and usage of I/O devices etc.
Pointer
|
Process States
|
Process Number
|
|
Program Counter
|
|
Registers
|
|
Memory Limits
|
|
List of Open files
|
|
….
|
|
Process Control Block