What is a Computer Program
- A computer program is a collection of instructions (written in logical order) that performs a specific task when executed by a computer.
- A computer executes the program's instructions in a central processing unit (CPU).
- A computer program is usually written by a computer programmer in a programming language e.g. Assembly language or C++.
- From the program in its human-readable form of source code, a compiler can derive machine code.
- Machine code—a form consisting of instructions that the computer can directly execute.
The Von Neumann Machine
The task of entering and altering programs for the ENIAC was tedious.
Von-Neuman gave the idea of a stored-program concept and his new stored-program computer is referred to as the IAS computer.
Stored-program concept: A program could be represented in a form suitable for storing in the memory alongside the data.(same memory)
Then, a computer could get its instructions by reading them from memory, and a program could be set or altered by setting the values of a portion of memory.
The IAS (Institute of Advanced Studies) computer, is the prototype of all subsequent general-purpose computers.
The IAS Computer
Four main components of the IAS computer are:
1) Main memory 2) ALU 3) Control unit 4) Input/Output (I/O)
The main memory, which stores both data and instructions.
An arithmetic and logic unit (ALU) capable of operating on binary data.
A control unit, which interprets the instructions in memory and causes them to be executed.
Input/Output (I/O) equipment operated by the control unit.
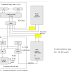
Structure of the IAS Computer
Stored Program concept.
Main memory stores programs and data.
ALU operates on binary data.
Control unit interprets instructions from memory and executes them.
Input and output equipment is operated by the control unit.
IAS Structural Components
These are addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
This requires a central arithmetic (ALU) part of the device to exist.
The logical control of the device, that is, the proper sequencing of its operations, can be most efficiently carried out by a central control (CU) organ.
Any device that is to carry out long and complicated sequences of operations (specifically of calculations) must have a memory unit.
The device must have organs to transfer information from the outside medium into its specific parts CPU and memory.
These organs form its input.
The device must have organs to transfer from its specific parts CPU and memory into the outside medium.
These organs form its output.
The Von-Neuman IAS Architecture
All of today’s computers have this same general structure and function and are thus referred to as von Neumann machines.
The main memory of the IAS consisted of 1000 storage locations, called words.
Each word has a width of 40 binary digits (bits). (1000 x 40-bit words)
Both data and instructions are stored there.
Numbers are represented in binary form, and each instruction is a binary code.
Each number is represented by a sign bit and a 39-bit value.